Introduction
In the vast realm of electronics, capacitors stand as silent heroes, playing a crucial role in various circuits and devices. These humble components store and release electrical energy, acting as essential building blocks in countless electronic systems. In this comprehensive exploration of capacitors, we will delve into their fundamental principles, types, applications, and the crucial role they play in shaping the landscape of modern technology.
The Basics of Capacitors
At its core, a capacitor is a two-terminal electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material known as a dielectric. When voltage is applied across the plates, an electric field is established, causing positive and negative charges to accumulate on the respective plates. This charge separation results in the storage of electrical energy within the capacitor.
Capacitance, measured in farads (F), quantifies a capacitor’s ability to store charge. The capacitance of a capacitor is directly proportional to the surface area of its plates, inversely proportional to the distance between the plates, and depends on the characteristics of the dielectric material.
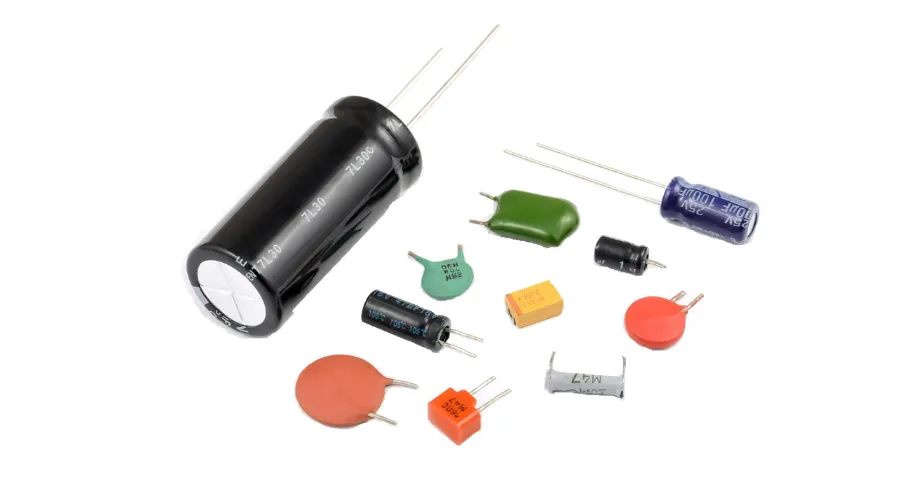
Types of Capacitors
Capacitors come in various shapes and sizes, each designed to suit specific applications. Let’s explore some common types of capacitors and their unique characteristics.
1. Electrolytic Capacitors
These capacitors utilize an electrolyte as their dielectric, allowing them to achieve high capacitance values in a compact form. Electrolytic capacitors are polarized, meaning they have a positive and a negative terminal. They find extensive use in power supply circuits, audio systems, and electronic devices requiring large capacitance values.
2. Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors employ ceramic materials as their dielectric. They come in different shapes and sizes, offering a wide range of capacitance values. Ceramic capacitors are widely used in high-frequency applications, such as radio frequency (RF) circuits and bypass capacitors in digital devices.
3. Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors use tantalum metal as the capacitor’s anode. They are known for their high volumetric efficiency and stable capacitance over a wide temperature range. Tantalum capacitors are commonly employed in compact electronic devices like smartphones and laptops.
4. Film Capacitors
Film capacitors use a thin plastic film as the dielectric. These capacitors offer high stability, low losses, and are suitable for applications requiring precision and reliability. Film capacitors find applications in audio circuits, power electronics, and lighting systems.
Capacitors in Action
Now that we have a foundational understanding of capacitors and their types, let’s explore their applications across various domains.
1. Energy Storage
Capacitors serve as vital components in energy storage systems. They play a key role in smoothing out fluctuations in power supply, reducing ripple voltage, and providing quick bursts of energy when needed. In applications like uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and electric vehicles, capacitors ensure a stable and reliable power source.
2. Signal Coupling and Decoupling
In electronic circuits, capacitors are frequently used for signal coupling and decoupling. Signal coupling involves the transfer of an AC signal from one part of a circuit to another, while decoupling involves isolating different sections of a circuit to prevent interference. Capacitors facilitate these functions, enhancing signal quality and minimizing unwanted noise.
3. Timing Circuits
Capacitors play a crucial role in timing circuits, where they control the rate of charge and discharge. Timing circuits are essential in applications like oscillators, pulse generators, and timers. Capacitors, in combination with resistors, determine the frequency and duration of electronic signals in these circuits.
4. Filtering
Capacitors are integral components in filter circuits, where they help smooth out AC signals by allowing certain frequencies to pass while blocking others. This filtering action is vital in audio systems, power supplies, and communication devices to ensure clean and reliable signals.
The Future of Capacitors: Advancements and Innovations
As technology advances, so do the capabilities and applications of capacitors. Researchers and engineers are continually pushing the boundaries to enhance capacitor performance and introduce new functionalities.
1. Supercapacitors
Supercapacitors, or ultracapacitors, represent a groundbreaking development in energy storage technology. These capacitors offer significantly higher energy density than traditional capacitors and can store and release energy rapidly. With applications in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and wearable electronics, supercapacitors are poised to revolutionize the way we store and utilize electrical energy.
2. Flexible and Printable Capacitors
The quest for flexible and printable electronics has led to the development of capacitors that can be integrated into flexible substrates. These capacitors open the door to innovative applications in wearable technology, flexible displays, and conformable electronic devices. The ability to print capacitors onto various surfaces also promises cost-effective manufacturing processes.
3. High-Frequency Capacitors for 5G Technology
As the world transitions to 5G technology, the demand for high-frequency capacitors is on the rise. Capacitors capable of operating at frequencies well into the gigahertz range are essential for the efficient functioning of 5G networks. Research and development in this area focus on creating capacitors with low losses and high reliability to meet the stringent requirements of 5G communication systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, capacitors, with their ability to store and release electrical energy, are indispensable components in the world of electronics. From powering everyday devices to enabling cutting-edge technologies, capacitors play a vital role in shaping the electronic landscape. As we look to the future, ongoing research and technological advancements promise to unlock new possibilities and applications for these versatile components. Whether it’s enhancing energy storage, improving signal quality, or enabling flexible electronics, capacitors continue to be at the forefront of innovation, driving progress in the ever-evolving field of electronics.