In the fast-paced realm of technology, electronic components play a pivotal role in powering the devices we use daily. From smartphones and laptops to intricate medical equipment and space exploration systems, electronic components are the building blocks that make modern electronics possible. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of electronic components, exploring their types, functions, and the crucial role they play in shaping the digital landscape.
Understanding Electronic Components
What are Electronic Components?
Electronic components are fundamental units that make up electronic circuits. These circuits, in turn, form the backbone of electronic devices. These components can be classified into two broad categories: active and passive components.
Active Components
Active components are those that can control the flow of electricity. Transistors, integrated circuits, and operational amplifiers are prime examples. These components are crucial for signal amplification, oscillation, and signal processing.
Passive Components
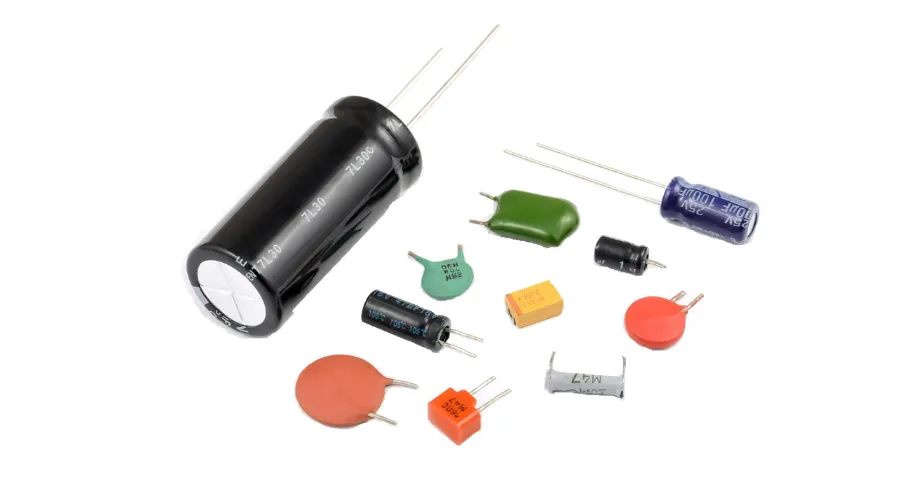
On the other hand, passive components do not possess the ability to control current by themselves. Resistors, capacitors, and inductors are common passive components. They play essential roles in regulating voltage, storing energy, and controlling the flow of electrical signals.
The Building Blocks of Electronics
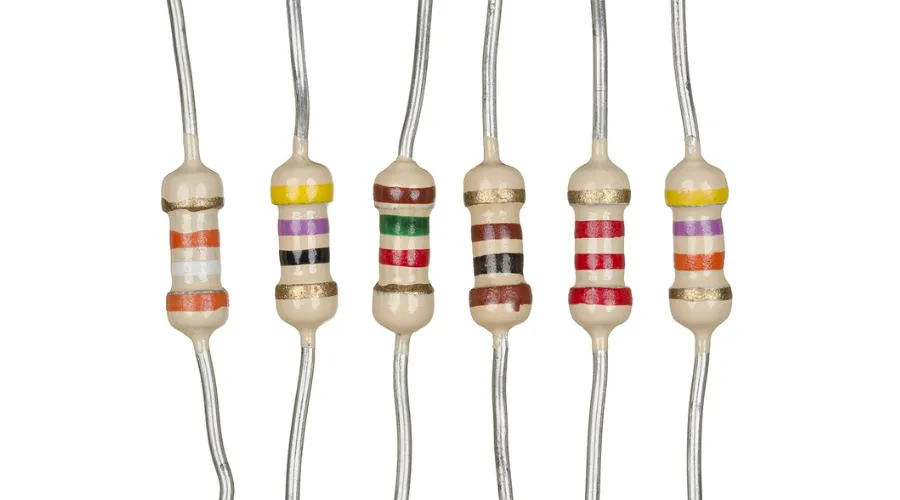
Resistors: Restricting the Flow
Resistors are among the most basic electronic components. They resist the flow of electric current, controlling its intensity. These components are crucial for adjusting signal levels, dividing voltages, and limiting current. Resistors come in various types, such as fixed resistors and variable resistors (potentiometers), providing flexibility in electronic circuit design.
Capacitors: Storing Energy
Capacitors store and release electrical energy. They consist of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. Capacitors are widely used for smoothing voltage fluctuations, filtering signals, and blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass.
Types of Capacitors
- Electrolytic Capacitors: These capacitors are known for their high capacitance and are commonly used in power supply circuits.
- Ceramic Capacitors: Compact and versatile, ceramic capacitors find applications in a variety of electronic devices.
- Film Capacitors: These capacitors offer stability and reliability, making them suitable for precision applications.
Inductors: Creating Magnetic Fields
Inductors store energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through them. They are vital components in transformers, motors, and inductance-based filters. Inductors resist changes in current, helping stabilize circuits and filtering signals.
Common Types of Inductors
- Coil Inductors: Consisting of wire wound into a coil, these inductors are prevalent in radio frequency applications.
- Toroidal Inductors: Shaped like a torus, these inductors minimize electromagnetic interference.
Advanced Electronic Components
Transistors: Amplifying Signals
Transistors are the workhorses of modern electronics. These semiconductor devices can amplify or switch electronic signals. They come in various types, including bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs), each serving specific purposes in electronic circuits.
Field-Effect Transistors (FETs)
FETs are widely used for their high input impedance and low output impedance. They play a crucial role in amplifying signals in various electronic devices, from audio amplifiers to radio-frequency amplifiers.
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs)
BJTs are versatile components that find applications in both amplification and signal switching. They are commonly used in audio amplifiers, oscillators, and digital logic circuits.
Integrated Circuits (ICs): The Heart of Electronics
Integrated circuits, or ICs, are compact assemblies of transistors, resistors, capacitors, and other components on a single chip. They revolutionized the electronics industry by enabling the creation of complex circuits in a small space. ICs are categorized into analog, digital, and mixed-signal types, each serving specific functions in electronic systems.
Analog Integrated Circuits
Analog ICs process continuous signals, crucial for applications like audio amplification and analog-to-digital conversion. Operational amplifiers (op-amps) and voltage regulators are examples of analog ICs.
Digital Integrated Circuits
Digital ICs operate with discrete signals, representing binary code (0s and 1s). Microprocessors, memory chips, and digital signal processors (DSPs) fall under this category. They are the brains behind computing devices and electronic systems.
The Impact of Electronic Components
The ubiquity of electronic components has transformed every aspect of our lives. From communication and entertainment to healthcare and transportation, electronic components have become indispensable.
Electronics in Communication
The evolution of communication systems, from telegrams to smartphones, owes much to electronic components. Amplifiers, oscillators, and modulators enable the transmission and reception of signals, making global communication seamless.
Electronics in Healthcare
In the medical field, electronic components power diagnostic equipment, monitoring devices, and life-saving machines. From the humble thermometer to advanced imaging systems like MRI and CT scanners, electronic components contribute to accurate diagnostics and patient care.
Electronics in Transportation
Modern vehicles rely on a myriad of electronic components for efficient and safe operation. Engine control units (ECUs), sensors, and communication systems work together to enhance fuel efficiency, optimize performance, and improve overall vehicle safety.
Electronics in Entertainment
The entertainment industry has undergone a revolution with the integration of electronic components. From high-fidelity audio systems to immersive virtual reality experiences, electronic components enhance our entertainment options and redefine the way we consume media.
Challenges and Future Trends
As electronic devices become more sophisticated, the demand for smaller, more efficient, and powerful components continues to grow. However, this progress comes with its own set of challenges.
Miniaturization Challenges
The push for smaller and more compact electronic devices poses challenges in terms of heat dissipation, power consumption, and manufacturing precision. Electronic components must evolve to meet these demands without compromising performance.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
With the increasing emphasis on sustainability, there is a growing need for electronic components that consume less power without sacrificing performance. Innovations in materials and design are essential for achieving greater energy efficiency.
Emerging Technologies
The future of electronic components is intertwined with emerging technologies such as quantum computing, flexible electronics, and bioelectronics. These advancements hold the promise of revolutionizing the capabilities of electronic devices, opening up new possibilities in computing, healthcare, and beyond.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electronic components are the unsung heroes powering the digital age. From the basic resistors and capacitors to the advanced integrated circuits, these components form the foundation of every electronic device we interact with daily. As technology continues to advance, the evolution of electronic components will shape the way we live, communicate, and explore the world. Embracing the challenges and opportunities on the horizon, the future of electronic components holds exciting possibilities for innovation and progress.